Acorn BBC Master
After commercial success of BBC Model B, BBC introduced Master as a home computer, suitable to teach IT and to be a home/small office computer. It has 128kB of RAM and feature-rich ROM, which contained BASIC, terminal, simple editor, spreadsheet and 2 disk file systems. BBC Master had good graphics capabilities and text modes, one of these modes was achieved by adding teletext rendering chip inside. Master had 2 cartridge slots and 3 free ROM sockets so it could be easily expanded. It featured ECONET, a low-cost local area network, which was useful in schools and small offices.
| Manufacturer | Acorn | |
| Origin | UK | |
| Year of unit | 1986 | |
| Year of introduction | 1986 | |
| End of production | 1993? | |
| CPU | MOS 65SC12 | |
| Speed | 2MHz | |
| RAM | 128K | |
| ROM | 128K (BASIC, Terminal, Editor, Spreadsheet, Disk File System) | |
| Colors: | Maximum 8 of 16 | |
| Sound: | 4-channel TI SN76489 | |
| OS: | MOS, BASIC, A/DFS | |
| Display modes: | 8 text/graphics modes. Up to 640x256 monochrome or 160x256 16-color. | |
| Media: |
Tape ROM Cartridge Floppy disk (controller built-in) |
|
|
Power supply: |
||
|
Built-in switching power supply Supplying +5V, +12V and -5V. External power output in the socket. |
||
| I/O: | ECONET Network Audio output Tape RS423 serial Analogue (4analog inputs, light pen) RGB Output Composite output (Monochrome!) RF modulator TUBE coprocessor bus 1MHz Bus User port Printer connector Floppy disk drive connector |
|
| Possible upgrades: | Inside: Modem, Econet, ROM upgrades... many. | |
| Software accessibility: | Dedicated: Not easy. Compatible earlier BBC: Easy. |
Dedicated accessories in collection: |
History of my unit is not much known. The only thing known is that it was purchased in UK and after a year moved to Poland. There it was used in hearing-impaired association somewhere in Silesia. It was used there until early 1990s. It's not known what happened next, as inside I found batteries manufactured in 1999, so it had to be used somewhere. Finally it was sent to recycling plant, from which I bought it.
Acorn BBC Master Compact
BBC Master Compact is a smaller version of BBC Master.
It has no cartridge slots, tape connector and RF modulator, but
preserves "sideways" connector for expansions. Some of expansion buses
available in a full Master are not included in Compact too.
Battery-backed settings memory has been replaced with a chip similar to
EEPROM, so Compact has no real time clock. Econet network support was
available only as expansion kit, as well as RS232 capability - 4 chips
had to be separately purchased and installed. Power supply and floppy
disk drive has been moved to external casing, usually placed under
monitor. The biggest improvement was floppy disk drive - this computer
based on a new format of disks, 3.5-inch. This situation allowed to fit
even 640kB on single disk, but cost of 3.5" disk was higher than 5.25"
disk, so the software could be even few times more expensive than
software on a 5.25" disk. It should be noticed that in a demo disk, BBC
Compact had a simple GUI application for launching sample programs.
Interestingly, Italian company Olivetti acquired most of Acorn's shares
in late 80s. They tried to spread Master Compact in Europe branding it
as Olivetti Prodest PC 128 S, but without bigger success.
| Manufacturer | Acorn | |
| Origin | UK | |
| Year of unit | 1986 | |
| Year of introduction | 1986 | |
| End of production | 1990? | |
| CPU | MOS 65SC02 | |
| Speed | 1.8MHz | |
| RAM | 128K | |
| ROM | 64kB (MOS, BASIC, ADFS) + expansions | |
| Colors: | Maximum 8 of 16 | |
| Sound: | 3-channel | |
| OS: | MOS, BASIC, ADFS | |
| Display modes: | 8 text/graphics modes. Up to 640x256 monochrome or 160x256 16-color. | |
| Media: |
ROM Cartridge Floppy disk (controller built-in) |
|
|
Power supply: |
||
|
1 - GND |
||
| I/O: | RGB Output Composite video output (mono) RS232 (if upgrade installed) Econet (if upgrade installed) Joystick/mouse Printer port Disk drive connector System bus expansion |
|
| Possible upgrades: | Inside: Serial, Econet, ROM upgrades... many. | |
| Software accessibility: | Dedicated: Not easy. Compatible earlier BBC: Easy. |
Dedicated accessories in collection: |
My unit is in unknown history. Someone added an audio output to it, later it survived flood. No other things are known.
| Contents: | Starting, battery, usage | Recording media | Pinouts | Links |
MASTER ONLY: Let's start with a battery.
(For Master Compact go directly to "Starting")
Battery is used by BBC Master to keep ROMs configuration
in one piece after electrolytic capacitors run out of energy (about 15
minutes after power off). In first units there was a single rechargeable
lithium battery used, placed near speaker, but it was very hard to buy
it. In later units there was a diode and the same size non-rechargeable
battery, but this size was also quite rare. Later Acorn used battery
pack built of 3 1.5V AA cells connected in series, inserted on the left
side of the computer case near the keyboard.
Now there are problems with rechargeable batteries, so it's good to have
a non-rechargeable battery pack. You need some casing to keep 3 AA 1.5V
batteries installed in series. Now, connect a 1N4001, 1N4005 or similar
diode to + lead of the battery, facing cathode AWAY from +, meaning the
bar away from +. To minimize current, install a 120Ohm resistor next to
diode. As in schematic:
-
----[-BATTERY1+]--[-BATTERY2+]--[-BATTERY3+]---[>|]--[120R]--- +
Now connect battery pack (with diodes) to BBC: look for PL8 connector on
the left edge of the mainboard. There are 3 pins. The pin closer to the
back of computer is ground, the middle pin is power. In most units both
pins on the edges are ground. Connect - to ground pin, + to the middle
pin. You are ready. See this drawing:
|
|
|PL8
| x <--connect pack's - here
| x <--connect pack's + here
| x
|
| _
|| |
After switching on, you should configure it.
1. RESET CMOS by switching Acorn on while pressing R key.
You should see:
CMOS RAM Reset
Press Break co continue
Press Break, you should get a beep and Acorn MOS starting, see:
Acorn MOS
This is not a language
*_
Type ROMS and press Enter. Now you can see all software installed in
system ROM. You can INSERT or UNPLUG software, which means the program
is enabled or disabled. Just type INSERT and number of ROM in decimal (ROMS
displays it as hex).
And you can type this to apply default configuration:
CO. BAUD 4
CO. NOBOOT
CO. CAPS
CO. DATA 4
CO. DELAY 50
CO. NOTUBE
CO. NODIR
CO. FDRIVE 0 //or 3 if you
experience problems
CO. FILE 13
CO. FLOPPY
CO. IGNORE 10
CO. LANG 12
CO. MODE 7
CO. LOUD
CO. PRINT 1
CO. REPEAT 10
CO. SCROLL
CO. TV 0,1
Explaination of options is in this text file.
Press Ctrl-Break . It's general key to reset the
computer entirely.
In Master Compact instead of battery, configuration can be made using control panel from boot disk. It will be written to EEPROM.
Starting:
It boots to MOS, Machine Operating System, which can start BASIC, ROM software or filesystems. If you use a filesystem, all BASIC commands such as CHAIN, LOAD, SAVE work with this filesystem. There could be tape (in Master only), ROM or disk filesystem, there are 2 disk filesystems: ADFS and DFS (In Compact only ADFS), both require properly formatted disk in drive to start.
SIMPLE MOS COMMANDS:
1. ROMS - displays list of ROM programs
2. UNPLUG x - unplugs ROM x (x is decimal)
3. INSERT x - inserts ROM x (x is decimal)
4. TIME - displays time from battery-backed RTC
5. WORD - starts View wordprocessor. Esc switches between command/workspace
(!)
6. SHEET - starts ViewSheet. Esc switches between command/workspace (!)
7. BASIC - goes to BASIC. From here you can order MOS by typing command
with *, for example *ROMS (!)
8. EDIT - launches text editor. (!)
9. KEYx - x is 0-9, assigns commands for f keys. For example
KEY0TIME|MROMS|M will producecurrent time and roms list. Use |M as
return key.
10. CONFIGURE - configures parameter.
11. MOTOR 0 or MOTOR 1 - turns cassette motor on or off, if you have
suitable recorder
12. TIME$ - setting time. Acorn is NOT Y2K compliant. In Compact
it returns only one value, 1999.
13. TERMINAL - starts terminal emulation (!)
(!) - if these do not work, make sure you have INSERTed
proper ROMs.
Any time when in BASIC, commands from *-prompt work by typing * before
them, e.g. *ROMS, *INSERT etc.
The computer can use 4 filesystems to access data on
tapes, floppies or cartridges in similar way. These are:
14. TAPE - Cassette File System
15. ROM - ROM file system - use RUN PROGNAME to run program from
cartridge
15. DISC - Disk file system, usually starts by itself if ADFS/DSF ROM is
inserted.
With BASIC:
CHAIN"PROGNAME" - loads and runs program
LOAD"PROGNAME" - loads BASIC program
SAVE"PROGNAME" - saves BASIC program
When using tape, message:
?BLock, ?Data or Rewind tape
means "I understand it, but don't know what is this thing" - the most
common source of this problem is the volume level bad.
WORKING WITH DISKS
DFS (Disk File System) and ADFS (Advanced Disk File System) are
switchable by pluggnig and unplugging ROMs, at least in my machine. DFS
is supplied for compatibility with BBC Micro Model B microcomputer.
In DFS, the commands
are the same (LOAD, SAVE, CHAIN) in BASIC, remember about drive number,
you can change them with *DRIVE x command. Two-sided disk drive is
virtually 2 drives unit!
There's something like directories in DFS - directories are
single-letter only, you can go to directory by typing DIR X (go to
directory X). This command is also valid:
SAVE :2.W.MEMO - saves file as MEMO in directory W in drive 2.
You can run machine-code program by typing just progran mane from MOS,
it'll cause current filesystem to load program and run it. For example:
*:2.W.UTILITY
How to display disk contents? CAT x - x is drive number.
ADFS has PC-like
directory structure, with hierarchical folders, BASIC commands are
normal (CHAIN, LOAD, SAVE), filesystem commands in BASIC must be
preceded by *.
*DIR GAMES - goes to directory GAMES
LOAD"GAMES.NUMBERS" loads file NUMBERS from directory GAMES.
Now it fou're in GAMES directory, and there's a PROGS directory on the
same level you can
*DIR $.PROGS
to go to the PROGS directory which is in root dir. $ IS THE ROOT
DIRECTORY. ^ is parent directory, so DIR ^ goes up, like CD .. in DOS.
*DIR :1 goes to side one, DIR :2 to side two.
*CDIR MYGAME - creates MYGAME directory in current folder.
*CAT - displays current directory contents
*CAT :2.BACKUP - displays contents of directory BACKUP on drive 2.
Simple, isn't it? More info can be found in manuals or here:
http://www.acornelectron.co.uk/eug/19/a-adfs.html
The disk is prone to fragmentation, as it can only store file in one
piece. So you have to defragment disk sometimes. Easy? Not so easy.
Because screen memory is used to temporarily store data, and blinking
cursor is arbitrarily set there, this cursor
destroys data!. And all data corrupts. Before compacting you
have to disable blinking cursor. Run BASIC, then type:
VDU23,1,0;0;0;0;
*COMPACT 40 3C
If, after running some program from disk, you hear
strange sounds and nothing happens, reset machine and check using ROMS
directive do you have BASIC ROM activated (INSERTed). If not, and you
try to execute BASIC program, computer may try to load it as machine
code and perform random writes to sound buffer causing this strange type
of "music".
That's what you should know for the beginning.
Master Compact Only: Mainboard
Serial port upgrade:
IC13: 6850 ACIA (serial port controller chip).
IC14 SERPROC ?2026? - Proprietary logic chip
IC5: MAX232
IC9: 74ALS169
Jumpers:
PL11 - if set towards connectors, IC38 ROM socket becomes non-active and
this ROM space is given to edge connector for expansions having own ROM.
Otherwise, it can be populated using in-computer ROM.
PL12 - if set towards connectors, system ROM (IC43) must be 64K.
Otherwise, 128K can be used. For future expansion.
ROM sockets IC29, IC23 and IC17 are for user's ROMs.
Recording media
There are 3 types of disks:
1. 40-track single density, 160K, sometimes called Small (S), ADF files
(not to be confused with Amiga ADF - different size), rarely ADL. If you
have an ordinary 5.25" floppy disk drive it's likely that it supports
only this mode.
2. 80-track single density, 360K, sometimes calles Medium (M) - ADF
files (not to be confused with Amiga ADF - different size), rarely ADM
3. 80-track, double-density, 640K, sometimes calles Lagre (L) - ADL
files. Can be copied to 3.5" floppy using OmniFlop. These will
work for Master Compact without problems as it has 3.5" drive.
SSD and DSD files are for DFS, not ADFS. It's hard to write it in most
PCs.
There's a tool called FDC, it may work on some PCs, but I haven't managed it to read/write any disk.
MAKING SYSTEM UTILITIES DISK IN 40-TRACK SYSTEM
It's a hard, manual procedure, if you have only
40-track drive, which was quite popular as cheapest disk-drive thing.
Here I'll describe how to mock-up a bootable 5.25" disk from 3.5"
utilities disk.
I. WHAT YOU NEED:
1.
OmniFlop and BBC Master Welcome and
Utilities disk image
2. A FDD ribbon cable with one 5.25" (edge) connector and 2 3.5" (pin)
connectors WITHOUT twist. It's not in every computer store, you should
make it.
3. 3.5" drive with DS0/DS1 select jumpers
4. 5.25" disks
5. One 3.5" disk
6. Acorn BBC Master with floppy drive
7. Power supply for 2 floppy drives
8. Lots of patience.
II. PROCEDURE:
1. Download OmniFlop and 3.5" BBC Master Welcome & Utilities disk image.
2. Install OmniFlop drivers, use OmniFlop to write BBC Master disk image
to 3.5" disk (you need to cover the hole opposite to write-protection
tab).
3. Find a 3.5" drive with DS jumpers, make it DS0. Take your 5.25" Acorn
drive, make it DS1.
4. Connect 3.5" and 5.25" floppy drives to BBC Master using cable.
5. Find a good power supply for both drives, as Acorn's may not survive
the load. AT power supply is good.
6. Turn everything on and configure Master for ADFS. It should boot ADFS
from 3.5" floppy.
7. In the menu: 3 [return] -> 1 [return] (Run AForm), format a few 5.25"
disks in drive 1, 5.25" 40-track drive (answers: 1,S,YES).
8. Now we can do this: go to * prompt, there:
DIR :1
CDIR LIBRARY
CDIR HELP
It should create 2 directories on 5.25" floppy. CAT to check.
9. Get back to menu, for example by resetting machine or pressing Return
if you entered prompt from menu. Choose FileCopy, then:
Answers: A, 0, $.LIBRARY, A, 1, $.LIBRARY, M, *
It'll ask, answer Y for everything EXCEPT Fonts, Italic, Pfont, thin,
warning.
One more time, there: A, 0, $.HELP, A, 1, $.HELP, M, *
It'll ask, answer Y for everything
One more time, there: A, 0, $, A, 1, $, M, *
It'll ask, answer Y for: !boot, ADFS_Utils, Catall, Copyfiles, Dircopy,
Exall, Harderror, Recover, RunAform, RunBackup, RunVeirfy
10. Go to * prompt. Type RENAME ADFS_Utils Utilities
11. Turn everything off, disconnect 3.5" drive, change 5.25" drive
jumper back to DS0.
12. Try new disk. It won't boot, but you should get * prompt. If you got,
type *OPT 4 3. Now reset to check will it boot. If it works, copy it
using Backup utility (~10-15 swaps needed) to another disk in case of
bad sectors.
This disk is NOT READABLE by 99% of PC FDD controllers, so I can't
submit an image here.
Terrible procedure, isn't it? But I checked, it works. I think it may be
easier with serial cable.
Cassettes may be stored in following formats:
- UEF - you need MakeUEF to create them from WAV and FreeUEF to play them
back to WAV.
- CSW - Cassette format made from WAV. You need CSW Viewer to create
/ play files.
- WAV - I think nothing to be explained here.
Important Pinouts:
RGB Pinout:
|
|
| 1 - Red 2 - Green 3 - Blue 4 - Sync 5 - GND 6 - +5V |
Tape connector (Master only):
|
|
| 1,4 - Output 2 - GND 3 - Input 5 - N.C. 6,7 - MOTOR CTRL RELAY |
RS423
|
|
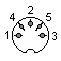
| 1 - Data in 2 - Data out 3 - GND 4 - CTS 5 - RTS |
ECONET:
|
|
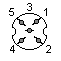
| 1 - Data+ 2 - GND 3 - CLOCK+ 4 - DATA- 5 - CLOCK- |
Analogue (Master only):
|
|
| 1 - +5V 2 - GND 3 - GND 4 - CH3 5 - Analog GND 6 - GND 7 - CH1 8 - Analog GND 9 - LPSTB 10 - PB1 11 - VREF 12 - CH2 13 - PB0 14 - VREF 15 - CH0 |
Floppy disk pinout is the same as in classic PC floppy drive - cable WITHOUT any twists, befire using PC drive select DS0 jumper in drive for drive 0, DS1 for drive 1 if you plan to use 2 drives (in newer drives jumpers may be made only as solder pads). BBC Master can use 3.5" disks, but woth hole opposite to write protection tab covered.
Master Compact Only:
Joystick:
|
|
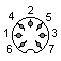
| 1 - PB3 2 - PB2 3 - PB1 4 - PB1 5 - CB1 6 - PB0 7 - +5V 8 - GND 9 - CB2 (whatever it means, based on service manual) |
Disk drive:
|
|
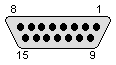
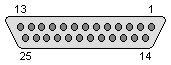
| 1 - INDEX 2 - /S0 3 - /S1 4 - NC 5 - /MOTOR 6 - /DIR 7 - /STEP 8 - /WRITE DATA 9 - /WRITE ENABLE 10 - /TRK0 11 - /WPROTECT 12 - /READ DATA 13 - /SIDE 14..25 - GND (according to service manual, verify with real hardware before using!) |
Links:
http://www.stairwaytohell.com/essentials/index.html?page=homepage
- General utilities
http://8bs.com/manuals.htm#manuals - Manuals for Acorn BBC computers
http://mdfs.net/ - Software for Acorn
http://web.archive.org/web/20120218121025/http://nvg.ntnu.no/bbc/xfer-conv.php3 - Transferring files
http://web.archive.org/web/20090130090248/http://bbcdocs.com/ -
Now-defunct site containing documentation.
http://www.stairwaytohell.com/
- BBC Micro and others archive.
http://web.archive.org/web/20100211082642/http://www.strafom.force9.co.uk/bbc/Retrobbc/Index.htm
- Some ROMs are still downloadable.
http://8bs.com/ - Much interesting stuff.
http://web.archive.org/web/20111205025318/http://bbc.nvg.org/ - "The BBC Lives!"
Master Compact:
http://chrisacorns.computinghistory.org.uk/docs/Acorn/Manuals/Manuals.html
- Service manuals and other documents
http://b-em.bbcmicro.com/ - Open
Source emulator
http://web.archive.org/web/*/http://b-em.bbcmicro.com/B-emv2.2Win.zip
- Windows version of above.
http://www.sprow.co.uk/bbc/howto.htm#colourcvbs - Colour
composite mods for some BBC computers