Acorn BBC Micro Model B
In 1980s British education authorities decided to
introduce some computer science teaching project. In the Computer
Literacy project IT teaching has been standardised to use single,
British computer types (Acorn,
Sinclair and Dragon computers
were considered, but finally Acorns have been chosen), unified teaching
program. BBC produced a TV series popularizing usage of microcomputers.
In their popularity peak, about 80% schools had BBC computers.
Acorn BBC Micro was Acorn's computer for schoold, but it could be
ordered for private use too. Inside, it had 32kB of RAM (Model A had
16kB) and 6502 CPU usually made by Rockwell. The machine had more I/O
ports than other British computers: Not only 1MHz bus expansion, but
also "Tube" bus, allowing to connect other processors to the computer.
Tube allows to connect second 6502 for graphics application or ARM
processor. BBC Micros equipped with ARM were used as development kits
for later Acorn ARM computers. Connecting Z80 to Tube could make BBC
Micro run CP/M programs.
For usage in schools Acorn used a low-cost, serial port based (RS422)
local area network called Econet. Not all BBC Micros had Econet
electronics installed, and installation of needed components sometimes
requires to replace ROM.
Some rare BBC Micro have TMS5220+TMS6100 chips installed. These chips
allow to synthesize speech.
BBC Micro, called "Beeb" was very popular and in UK it's still popular
in hobbyist's workshops. Still (2015) there are many Internet pages
about it and they are usually still maintained.
| Manufacturer | Acorn | |
| Origin | UK | |
| Year of unit | 1984? | |
| Year of introduction | 1982 | |
| End of production | ??? | |
| CPU | MOS 6502 | |
| Speed | 1.8MHz | |
| RAM | 32K | |
| ROM | Depends on user, usually ca. 32kB | |
| Colors: | Maximum 16 | |
| Sound: | 3 channels | |
| OS: | BASIC, own ROM | |
| Display modes: | Text: 40x25 (teletext),
20x32, 40x25, 40x32, 80x32, 80x25 Graphics: 160x256x16 colors, 320x256x4 colors, 640x256x4 colors. |
|
| Media: |
Tape, disk drive, ROM expansions. |
|
|
Power supply: |
||
|
Built-in switching power supply |
||
| I/O: | System bus, 1MHz Bus TUBE expansion FDD connector User port Printer port RF out, RGB out, composite out RS423 Cassette port Analog joystick input Econet local network |
|
| Possible upgrades: | Many expansions using 1MHz bus, Tube bus or serial/parallel ports. | |
| Software accessibility: | Quite easy (TOSEC, sites) |
My unit probably comes from school, because it has a
complete Econet set on board. It has also connector for Solidisk
expansion card (but no board fitted). Solidisk was a board which was inserted into edge
connector installed into one of ROM sockets. Because ROM sockets don't
provide all CPU signals, it was needed to connect few wires soldering
them directly to chips. The Solidisk expansion card provided two ROM
sockets and additional 32K of memory.
My unit has also additional ROM with Edword text editing software.
Now about British plugs.
Until 1992 British home electric devices were sold without mains plug. If your
house had European sockets, you installed European plug. If, like most
houses in UK, you had British sockets, you installed British standard
(Type G) plug. These plugs were available even in normal stores all over
country.
In BBC Micro you may see that the plug is not manually mounted - it's a
plastic moulded plug on a cable. The legal requirement to supply devices
without plug was in order with home-use devices. BBC Micro computers
were made under specification for British education, where British
sockets were (and still are) in use. National orders were exceptions of
this rule.
If your BBC has problem with starting, check power supply and its capacitors. 230V filtering capacitors and electrolytic ones may be damaged, as they may leak after long time.
| Contents: | Starting, usage | Recording media | Pinouts | Links |
Starting
The machine just boots up to Acorn BASIC or, depending
on configuration, contents of some ROM.
Versions with ECONET network support may display its number and "no
clock" which maens that there is no network connected (Econet was quite
similar to Polish Junet, but Acorn
used better cables and more reliable transmission). BASIC is quite
conventional, but is has a few significant features. Except Basic
commands there are * comands, starting with character *. These commands
address the ROM directly. The most important are:
*TAPE - switches tape as the main storage. In the opposite is *DISC.
*SAVE, *LOAD - saves and loads machine-code software from main storage.
*[name] - Starts [name] program from ROM.
In BASIC, you can load and save BASIC programs using
LOAD "program" and SAVE "program" commands.
Before running program from ROM, make sure that you have set a proper
main storage. If you try to run program from ROM with DISC storage while
there is no disk drive present, it will not work properly.
Recording media
See Acorn BBC Master, as it has similar disk system (DFS, not ADFS!)
Important Pinouts:
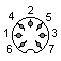
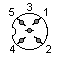
RGB Pinout:
|
|
| 1 - Red 2 - Green 3 - Blue 4 - Sync 5 - GND 6 - +5V |
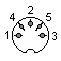
Tape connector:
|
|
| 1,4 - Output 2 - GND 3 - Input 5 - N.C. 6,7 - MOTOR CTRL RELAY |
RS423:
|
|
| 1 - CtS 2 - RtS 3 - GND 4 - Data in 5 - Data out |
Econet:
|
|
| 1 - Data+ 2 - GND 3 - Clock+ 4 - Data- 5 - Clock- |
More pinouts can be found in this document.
Links:
http://www.ncus.org.uk/dsbbcoms.htm - BBC Micro user's guide
http://web.archive.org/web/20150424210800/http://rk.nvg.ntnu.no/bbc/doc/A%20Hardware%20Guide%20for%20the%20BBC%20Microcomputer/bbc_hw_04.htm
- Link settings
http://www.ncus.org.uk/dsbbcoms.htm - BASIC commands
http://telcontar.net/About/Beeb/ - Expansion, which in part is
presented in this page
http://chrisacorns.computinghistory.org.uk/Pics/BBCB7LL.html - Nice
mainboard photo
http://bbc.nvg.org/ -
File archive, many technical manuals and programs
http://chrisacorns.computinghistory.org.uk/ - Everything related to
Acorn
http://primrosebank.net/computers/bbc/floppy_drives.htm - Which
floppy driver work with BBC?
http://www.sprow.co.uk/bbc/doctor.htm - Hardware faults symptoms and
how to fix them
http://www.bbcmicrogames.com/acornsoft.html - Games for download!
http://www.stairwaytohell.com/menu.html - Disk images, software,
ROMs
http://wouter.bbcmicro.net/ -
He has a big ROM archive, cover sacne and technical descriptions
http://b-em.bbcmicro.com/ - How
about an emulator? ;)
You can also watch
the original
Computer Programme from BBC Television.