The unit selection technique is that described in [6]. In this technique, units of the same type are collected together and an acoustic distance is calculated between each occurrence. A recursive splitting algorithm is used to find which high level questions can be used to split the data such that the mean acoustic distance between members of the partition is minimized. Thus clusters of acoustically similar units are indexed by trees of high level questions.
More formally, we define the acoustic distance ![]() between
two units
between
two units ![]() , and
, and ![]() where
where ![]() as
as
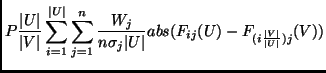
We can then define the impurity of a cluster as
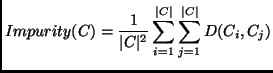
The acoustic distance between each unit is calculated from the mahalanois euclidean distance between pitch synchronous vectors of Mel cepstrum coefficients plus coefficients for duration and F0.
This method is designed to automatically distinguish between acoustically distinct units based on context. It is this particular factor that we are exploiting in this case. As we are assuming no phonetic knowledge, the acoustics and letter contexts (plus higher level information) are being used to define the units that will be selected at run time.