Robotron KC87 (KC 85/1, Z 9001)
In all Eastern Block countries Eastern Germany had a
very good location, allowing for better technology development. It was
very hard to buy western electronic components, but contrary to e.g.
Soviet Union it was possible. In 1980s many home computers have been
designed in GDR, they were usually incompatible with each other. Many
plants in Robotron combinate manufactured different home computers.
In 1984, Dresden Messelektronik factory started manufacturing Robotron
Z9001 computer. It was a small computer with 16K of RAM and Z80 CPU. It
was expandable with 4 modules. In 1985, after releasing of KC85/2 by
factory in Muhlhausen, they renamed Z9001 do KC85/1, to complete series.
Of course KC85/1 was totally incompatible with KC85/2 or /3.
In 1987 Dresden plant rebranded KC85/1 to KC87 and manufactured it until
1989.
It was quite robust computer system, first units had monochrome screen
adapters, later had color (one joystick port was modified to become RGB
output and both joysticks shared the same connector). Screen adapters
were installed on small expansion boards inside computer. Earlier units
had no BASIC in ROM, so it had to be loaded from tape or provided in
external module. During development, computer got many improvements:
BASIC in ROM, K565RU6 RAM chips (like 4116, but they don't need 12V and
-5V) or extended I/O port.
| Manufacturer | VEB Robotron Messelektronik "Otto Schon" Dresden (part of Robotron kombinat) | |
| Origin | East Germany | |
| Year of unit | 1987 | |
| Year of introduction | 1984 (As Z9001) | |
| End of production | 1989 | |
| CPU | Z80 | |
| Speed | 2,5MHz | |
| RAM | 16kB | |
| ROM | 16kB | |
| Colors: | 16 (or monochrome) | |
| Sound: | Simple beeper, built-in | |
| OS: | KC87 OS (and Basic) | |
| Display modes: | 40x24 character/semigraphic mode | |
| Media: | Magnetic tape |
Power supply: |
|
|
||
|
Built-in semi-switching power supply giving +5V, -5V, -12V, +12V DC. Later units used +12V DC only for TV modulator and -5V for tape amplifier, -12V is unused in them.
Rating of Power Supply is: |
||
| I/O: | TV RF out RGB Out Tape In/out 1 connector for 2 joysticks User I/O connector 4 modules expansion (earlier there were 2 joystick connectors, one instead of RGB connector) |
|
| Possible upgrades: | Modules | |
| Peripherals in collection: - RFT LC-R tape recorder |
||
| Software accessibility: | TOSEC | |
My unit came in after-service state, but it was "serviced" by some moron many years ago and then stored in a basement. During servicing it has been opened, then faulty memory chip has been replaced and unit has been reassembled, then turned on. Because someone missed +5V and +12V wires, I had to replace CPU, EPROMs and about 75% of logic before it turned on. 12V blown only one chip of RAM. The replaced one.
If you want to diagnose it, look how GRAPHIC led behaves
when you turn it on. It should stay off or blink quickly, being lit when
PIO is uninitialized. If it lights steadily, it usually means that CPU
can't initialize PIO - CPU is not working or CPU/PIO/Logic is bad.
East German ROMs are also prone to failures.
| Contents | Loading programs | Making cassettes | Pinouts | Links |
Loading programs
After powering up, the computer should display garbage on screen, then clear it (by scrolling upwards) and output "robotron Z9001 OS" prompt. Then the following commands may be used:
BASIC - runs Basic from ROM. Asks for MEMORY END, usually
this is left blank and Enter is pressed, then you are in Basic.
In Basic, you can run CLOAD "PROGRAMNAME" to load software from tape.
To Load machine-code program, don't enter Basic, but just type its name, then press Enter. You'll get "start tape" prompt and program will be loaded.
Making programs on cassette:
The method for BASIC programs (in .SSS format) is
similar to one from KC85/4. There is a data converter in
JKCEMU emulator which
can convert between SSS format and a WAV file, but you won't get proper
headers as it just rips memory and encodes it to WAV. Better WAVs are generated by toolchain
of KCEMU emulator. Download it freely from
author's site
looking for "Kassetten transfer" file (kcload.zip). Then select:
- Automatische speichern - checked
- Kodierung: KC85/1..4, KC87
- In: as selected by program.
- Out: Datei KCLOAD.WAV
Now click "Speichern auf Kassette..." and select
SSS file.
The file will be rendered to KCLOAD.WAV.
If it doesn't work either, there's a modified version of
KCLOAD program downloadable here:
http://hc-ddr.hucki.net/wiki/doku.php/programme:kassetten_faq
It can also process machine-code programs stored in COM files!
In every program, it's good to try with all converters, JKCEMU, KCEMU and KCEMU with modification. JKCEMU will show you starting addresses. To run converter in JKCEMU click Extra->Werkzeuge->Dateikonverter.
Pinouts:
All as seen from the user side, not the opposite one:
Cassette port:
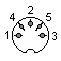
1 - Cassette OUT
2 - GND
3 - Cassette IN
4 - nc
5 - nc
RGB port:

1 - G
2 - B
3 - SYNC
4 - R
5 - +5V
Shield - Ground
Joystick connector unknown.
Useful links (Warning: in German):
-
http://www.sax.de/~zander/index2h.html - Look in "Hobby" / KC87 -
lots of useful documentation
-
http://hc-ddr.hucki.net/wiki/doku.php/z9001 - Nice site with tapes,
documentation and information.
-
http://www.robotrontechnik.de/index.htm?/html/computer/kc_dresden.htm
- At RobotronTechnik
-
http://www.jens-mueller.org/jkcemu/ - JKCEMU emulator
-
http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Z_9001,_KC_85/1,_KC_87 - German
Wikipedia page of Robotron KC87 with prototype photo.