Apple IIc (//c)
Apple II computers weren't much popular in Poland. In
USA they were widely used and there was much software developed for it.
The first Apple II was a 6502-based computer with Integer BASIC. The
cause of its popularity was possibility to expand system unit with
boards. However the IIc (C for Compact) was not expandable as older
Apple IIs.
Apple IIc had quite good graphics capabilities for its time, and
1-channel speaker. In Apple II series storing data and programs on
floppy disks became common. As first Apple II computers had cassette
interface, IIc doesn't have one.
| Manufacturer | Apple Computers | |
| Origin | U.S.A | |
| Year of unit | 1986 | |
| Year of introduction | 1984 | |
| End of production | 1990 | |
| CPU | MOS 65c02 | |
| Speed | 1MHz | |
| RAM | 128K | |
| ROM | 16kB (Basic) | |
| Colors: | 16 | |
| Sound: | One-channel built-in speaker. | |
| OS: | Applesoft BASIC, ProDOS, Apple DOS 3.3. | |
| Display modes: | Text: 40x24, 80x25 Graphics: 40,80x48x16, 140,280x192x16, 560x192x2 |
|
| Media: |
Built-in 5.25" FDD External 5.25" FDD |
|
|
Power supply: |
||
|
7-pin DIN Male: 6,7 - Not connected |
||
| I/O: | Composite monitor (RCA) RGB monitor (Apple flat panel) Joystick/mouse External FDD 2x serial ports Earphone jack |
|
| Possible upgrades: | Memory upgrade slot. | |
| Software accessibility: | Easy (TOSEC, dedicated sites) |
My unit came with a strange DIY power supply. This power supply is made in universal casing and contains transformer, diode bridge and capacitors - nothing more. No regulation, no stabilization. Voltage output is 13.75V DC. Computer works properly even if it drops to 12.75. There's another winding on transformer giving 120V AC to monitor.
| Contents: | Starting | Making system floppies | Mouse | Serial Communication | Links |
Starting:
You can boot it to BASIC or boot it with floppy disk. By
booting it from floppy, you can load Basic-like EsDOS or ProDOS.
TO BOOT TO BASIC: Turn it on without floppy and quickly press Ctrl-Reset.
Making system floppies:
See ADTPro in Links section. You will have to make a serial
cable to connect your comuter's serial port to Apple.
http://adtpro.sourceforge.net/bootstrap.html - see "Starting from
bare metal".
Few hints about procedure described in link above:
Remember to type the letter "B" in "14B" or "10B" in lower case!
Another thing is getting a disk image to Apple II, called Receiving -
you just need to establish connection, run ADT on Apple II and use
Receive command typing file name (file in PCs working directory, which
can be set in ADTPros menus). PC will act as server to Apple II. But
remember to INITialize or FORMAT (in ProDOS, ADTPro command letter F)
all disks before writing!
If your bootstrapping went OK, but you can't receive and it stops on
block 1, you should fiddle with connection speed - not only lower, for
me it hung with 9600bps but worked well in 115200. If you change it in
PC remember to do the same thing on Apple side.
In esDOS, if you format a floppy, it becomes automatically bootable.
In ProDOS, you have to Receive a bootable floppy.
Remember that NIB floppy images are nibbled (half-byte) images and they
may contain copy-protected data impossible to write using Apple IIc's
drive!
Remember, these disks are written on one side, by cutting a write
protection hole in them symetrically you can flip it and format second
side of disk to be used.
Most programs just boot off the disks when computer is started with
them.
Mouse
Here is brief description of mouse pinout. Connector is DB9 female on the computer:
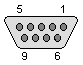
| 1 - Mouse ID - ? 2 - +5V 3 - GND 4 - X direction (TTL) 5 - X move (TTL) |
6 - not connected 7 -Mouse button 8 - Y direction (TTL) 9 - Y move (TTL) |
As you can see, it's not possible to connect my universal mouse to it. You need at least to build a phase detector to drive direction inputs. More, I don't know should I short ID to ground, 5V or put some data here.
Serial communication
The computer has 2 serial ports, one for printer and one for modem. They can be used to communicate with PC COM port. It's accessible via DIN 5 female socket:
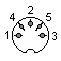
| 1 - Handshake out (DTR) 2 -Ground 3 -Handshake in (DSR) 4 -Data out (Transmit, TxD) 5 -Data in (Receive, RxD) |
Links:
http://adtpro.sourceforge.net - software and cabling to transfer
data from/to Apple II
http://www.virtualapple.org/
- Games to download. GONE - archive has been deleted. Try with file
names.
http://web.archive.org/web/20130107234016/http://www.retrocpu.com/apple-ii/games/ - More games
descriptions
ftp://ftp.apple.asimov.net/pub/apple_II/images/ - Big games and
software archive.
http://web.archive.org/web/20130405064741/http://www.vectronicsappleworld.com/basement/lead.html - Smaller
software archive
http://www.vectronicsappleworld.com/ - Archive of Apple II related
texts (archive
link if something doesn't work).
http://www.umich.edu/~archive/apple2/ - More software!
http://mirrors.apple2.org.za/ground.icaen.uiowa.edu/ - Another
software acrhive.
http://web.archive.org/web/20100413152530/http://apple2info.net/ -
Some useful programs.
http://www.callapple.org/ -
General site about older Apple computers. Blog, but worth looking at.
http://www.applevault.com/ -
Some scans and software
http://apple1.chez.com/Apple2cDskArchive/index.htm - Nice site about
Apple IIc
http://web.archive.org/web/20160306094749/http://www.apple2scans.net/ - Scans of
Apple-II related books and documentation.
http://web.archive.org/web/20090602032152/http://home.swbell.net/rubywand/A2FAQs4MAJORSITES.html
- Archived link list.
http://www.angelfire.com/80s/apple2/ - Here you can see original
game covers
http://web.archive.org/web/20130506052746/http://www.vectronicsappleworld.com/appleii/dos.html - DOS and ProDOS
Guide
http://www.1000bit.it/scheda.asp?id=2 - Scanned Manuals.