Amstrad (Schneider) CPC464
Not much popular in Poland, more known in France,
Spain and Portugal, this Z80-based home computer (CPC - Color Personal
Computer) has quite nice capabilities and realizes "all in one"
convention. The power supply is built in a specialized monitor, and the
computer itself has built-in tape recorder or 3" floppy disk drive.
That's why it wasn't popular - in eastern Europe a complete set was too
expensive for home user, and small screen of dedicated monitor was not
good for gaming.
In western Europe it was a good agreement between price and capabilities.
In multimedia it wasn't as strong as machines of its day, but built-in
BASIC was really fast and allowed for hardware interrupts.
These computers were re-branded many times and many units are already
prepared for it. In the minboard you can find LK1 LK2 and LK3 jumpers
described
Here, giving a variety of brands on startup screen: Amstrad,
Schneider, Orion, Awa, Solavox, Saisho, Triumph, ISP. The Link 4 is
responsible for 50Hz refreshing (if cut).
| Manufacturer | Amstrad | |
| Origin | UK | |
| Year of unit | 1987 | |
| Year of introduction | 1984 | |
| End of production | 1990 | |
| CPU | Z80 | |
| Speed | 4MHz | |
| RAM | 64K | |
| ROM | 32kB (Basic) | |
| Colors: | 27 | |
| Sound: | 3-channel | |
| OS: | Locomitove BASIC. | |
| Display modes: | Text: 20x25x16c,
40x25x4c, 80x25x2c. Graphics: 160x200x16c, 320x200x4c, 640x200x2c. |
|
| Media: | Built-in tape recorder. | |
|
Power supply: |
||
|
A female DC Jack (fi=5.5m, inside 2.1mm) on
the computer. |
||
| I/O: | Printer port (7-bit) System bus (known as floppy port) Joystick connector Amstrad Monitor Stereo jack sound output (to the amp). |
|
| Possible upgrades: | A few, memory upgrade requires programmable chips. | |
| Accessories in collection: | ||
| Software accessibility: | Quite easy (FTP, TOSEC, a few dedicated sites) |
It's impossible to connect a floppy drive to it without a special controller. The floppy drive port is a system bus, in which this controller communicated.
And there were a few versions of these computers:
- A normal Amstrad CPC464, shown in picture in this page. These
were at least 3 versions - one with full-length mainboard, second, newer,
with much shorter (more than a half) one and third, very small based on
PLA chips. The last 2 versions have joystick and audio connectors on the
left, not rear.
- Schneider CPC464 - CPC464 for german market, with coloured special keys,
German RF shielding and rarely connectors (because of restrictive EM
interferences law in Germany all edge connectors had to be replaced with
Centronics-like connectors), and sometimes with keyboard software and
sticker replacing QWERTY to QWERTZ.
- CPC472 - Another result of democracy's legislation. In Spain, all
computers with random access memory less or equal to 64K had to be
localized with code page, keyboard and system software. In such
optimized BASIC even translating messages may lead to incompatibility,
so Amstrad installed additional memory to reach 72K, so the entire
software modification was not necessary. This additional 8K of memory
was sitting on daughterboard and was not connected at all! A month after
CPC472 release, the law was changed and CPC472 has been discontinued.
Amstrad (Schneider) CPC6128
The 6128 has a built-in floppy drive instead of tape
recorder. Tape still can be connected externally. Another upgrade was a
memory, using 2 64K banks giving 128K.
Internal floppy drive allows to run CP/M 2 or CP/M+, but it is quite
slow. It was not much popular.
My version is branded Schneider, it's german re-brand of Amstrad. It is
also equipped with Centronics-like connectors for peripherals instead of
edge connectors because of german EM interference prevention law.
These computers were re-branded many times and many units are already
prepared for it. In the minboard you can find LK1 LK2 and LK3 jumpers
described
Here, giving a variety of brands on startup screen: Amstrad,
Schneider, Orion, Awa, Solavox, Saisho, Triumph, ISP.
| Manufacturer | Amstrad | |
| Origin | UK | |
| Year of unit | 1988 | |
| Year of introduction | 1985 | |
| End of production | 1990 | |
| CPU | Z80 | |
| Speed | 4MHz | |
| RAM | 128K | |
| ROM | 48kB (Basic) | |
| Colors: | 27 | |
| Sound: | 3-channel chip | |
| OS: | Locomotive BASIC,Amsdos | |
| Display modes: | Text: 20x25x16c,
40x25x4c, 80x25x2c. Graphics: 160x200x16c, 320x200x4c, 640x200x2c. |
|
| Media: |
Internal 3" Floppy disk drive Tape recorder connector |
|
|
Power supply: |
||
|
Two DC connectors: On the computer: |
||
| I/O: | Printer port (7-bit) System bus Joystick connector FDD connector Amstrad monitor connector Tape connector Stereo jack sound output (to the amplifier) |
|
| Possible upgrades: | A few, memory upgrade requires special programmable chip | |
|
Notice reversed polarity for 12V male plug! |
||
|
Reversing it will DAMAGE YOUR COMPUTER! |
||
| Accessories in collection: | ||
| Software accessibility: | Quite easy (TOSEC, FTP, dedicated sites) |
| Contents: | Starting | Image file formats | Recording media | Pinouts | Links |
Starting:
It boots to Locomotive BASIC. If machine has a floppy
built-in, it's already equipped with AMSDOS commands.
Running software from tape:
|TAPE
RUN"
It'll load and run program.
Running from disc uses commands:
CAT - displays directory listing
RUN"prog" - runs program prog.
|CPM - tries to load CP/M from disk
RUN"DISC - tries to auto-run disk.
|A, |B - changes active floppy
BAS and BIN files may be loadable.
Image file formats:
DSK - A Amstrad CPC disk format. Many emulators support it.
TZX - Tape format designed by Tomaz Kac, it is optimized
for exact data and can save tapes with strange loaders etc.
TAP - Tape format, it's optimized sound file.
CDT - It's TZX, and the extension means that this program is especially
for CPC.
Recording media
To get BAS files from disk to tape, you have to extract
it using CPCFS program.
The files got from this procedure are fed to CPC2TAPE, which modulates
them into TZX.
Resulting CDT file is TZX, so you have to play it using
Taper. There's
also a alpha version of TZX plugin for WinAmp (see my fileland), but
it's not tested. The best thing for today's OS and sound card is
WinTZX. It handles TAP files too.
Reverse procedure seems likely the same as in Spectrum. You can also use
CpcTapeXP (see links) to get TZX from WAV file.
Transfering disks is more difficult. You can connect
3.5" drive to CPC and use it, or you can connect 3" drive from CPC to
PC.
Another thing is getting CPCEMU15 from my fileland and reading Section 5
of its manual file. You need to build a special cable (use the plug from
5.25" disk drive ribbon cable if you have edge connector), but it'll
work.
Pinouts:
Audio and video connectors:
| CPC Audio | CPC Video |
Connecting to SCART TV |
| 3.5mm Jack: ]===---> 1 2 3 |
|
|
1 - Ground 2 - Right 3 - Left |
1 - Red 2 - Green 3 - Blue 4 - Sync 5 - Ground 6 - Luminance |
15 11 7 16 17 20 4 2 6 |
Theoretically it could be possible to get monochrome o/p with Luminance.
It's possible to connect Amstrad to TV with SCART RGB input, but remember that you still need a power source for it.
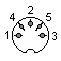
Joystick port Male DB9 (view from rear of computer):
 |
| 1 - Up 2 - Down 3 - Left 4 - Right 5 - Fire 3 6 - Fire 2 7 - Fire 1 8 - Ground 1 9 - Ground 2 |
(it's compatible with Atari Joysticks)
Another thing are these 2 grounds. Joysticks work by shorting direction/fire pins to ground. Two grounds are for 2 joysticks - you can connect two joysticks to this port at once by connecting their pins in parallel except ground - Ground 1 goes to Joystick 0's ground, Ground 2 to Joy 1's ground.
Printer port pinout (view from rear of computer):
|
35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 (centronics type port changes pins by 1 on lower row) (pinout is for edge connector) |
|
| 1 - /STROBE (11) 2 - D0 3 - D1 4 - D2 5 - D3 (15) 6 - D4 (13) 7 - D5 (12) 8 - D6 (10) 9 - GND (as D7) 10 NC |
11 - BUSY
(2) 12-13 - NC 14 - GND 15 - NC 16 - GND 17, 18(19) - NC 19 - GND (19) 20-18 - GND 29-32 - NC 33 - GND 34 - NC |
To construct parallel cable to PC, you have to connect 7 pins from this
port with pins in PCs parallel port. Numbers of pins in PC parallel port
are written in grey.
CPC464 Floppy port (or system bus expansion):
|
|
||||
| 1 - SOUND 2 - GND 3 - A15 4 - A14 5 - A13 6 - A12 7 - A11 8 - A10 9 - A9 10 A8 |
11 - A7 12 - A6 13 - A5 14 - A4 15 - A3 16 - A2 17 - A1 18 - A0 19 - D7 20 - D6 |
21 - D5 22 - D4 23 - D3 24 - D2 25 - D1 26 - D0 27 - Vcc (+5V) 28 - /MREQ 29 - /M1 30 - /RFSH |
31 - /IORQ 32 - /RD 33 - /WR 34 - /HALT 35 - /INT 36 - /NMI 37 - /BUSRD 38 - /BUSAK 39 - READY 40 - /BUS RESET |
41 - /RESET 42 - /ROMEN 43 - ROMDIS 44 - /RAMRD 45 - RAMDIS 46 - CURSOR 47 - LPEN 48 - /EXP 49 - GND 50 - CPUCLK |
There are 2 handy hardware hacks, with this port. The first one is
installing a momentary pushbutton between pin 40 and 49 (GND), it's a
system reset button.
The second one requires installing a toggle switch betewwn pin 39 and 49
- this switch allows to pause a whole computer in any moment!. After
pausing, the pins are disconnected and CPC continues work.
6128 Tape connector
|
|
| 1 - Switch 2 - GND 3 - Switch 4 - IN (to PHONE of tape rec.) 5 - OUT (to MIC of tape rec.) |
Links:
ftp://ftp.nvg.ntnu.no/pub/cpc/ - CPC file archive.
ftp://ftp.lip6.fr/pub/amstrad/
- connect here using FTP client, many utilities. If some file does not
exist it usually means that there's a new version.
http://web.archive.org/web/20130404132238/http://tacgr.emuunlim.com:80/ - A
CPC website.
http://www.ulrich-cordes.de/cpc/english/disk.htm - Connect PC drive
to CPC6128 - German one.
http://cpcwiki.eu/index.php/Guide_on_how_to_connect_a_3.5%22_drive_to_a_CPC6128/664
- connect a PC floppy drive to CPC6x
http://web.archive.org/web/20080223190637/http://perso.wanadoo.es/jaimegs/ordenadores/amstrad/3,5ext.htm
- Here's a modification with these switches. Spanish only.
http://www.fvempel.nl/3pc.html
- Connect Amstrad 3" drive to PC. 22DISK is accessible in my fileland.
http://web.archive.org/web/20130420195731/http://usuarios.multimania.es/putusoft/emucpc/menue.htm - Here
you'll find many interesting info about Amstrad CPC mods, hacks etc.
http://amstrad.eu/modules/TDMDownloads/viewcat.php?cid=13
- Utilities, e.g. to copy DSK to PC 3.5" disk
http://amstrad.eu/modules/TDMDownloads/viewcat.php?cid=23 - Download Amstrad
documentation, Search if you can't find.
http://www.cpcmania.com/ - Home
of CPCDiskXP, a tool for floppy i/o on PC and CPCTapeXP, a toold for
tape io.
http://genesis8.free.fr/index.php or
https://www.genesis8bit.fr/index.php - More utilities
http://web.archive.org/web/20060829231046/http://andercheran.aiind.upv.es/~amstrad/default.html
- starting point for closed website researching.
http://www.symbos.de/index.htm
- A GUI operating system for Amstrad, unfortunately requires much memory.
http://web.archive.org/web/20110711061920/http://cpcoxygen.fxwebdevelopment.com/ - A CPC Magazine.
http://www.arnimedes.de/ - A CPC
Emulator for DOS
http://problemkaputt.de/cpc.htm - Another not much known emulator,
versions for DOS and Windows.
http://www.winape.net/ - This is
probably the most recent emulator for Windows.